Case Breakdown: Movie Baadshah
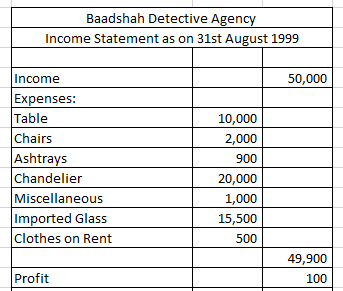
The scene that you just saw shows Raj, (played by Shahrukh Khan) who runs his own company called ‘Badshah Detective Agency’. While solving the first case, the company earns an income of Rs. 50,000 and the expenses of the company amount to Rs. 49,900.
In this blog, Learning Perspectives will explore the meaning of expenses in an organization.
What is Expense?
Any costs that companies incur for the generation of revenue are called expenses. When a company is a manufacturing company i.e. when the company produces something that could be cars, biscuits, cloth, etc. In those companies, different types of costs are shown in the income statement. These costs are related to the production of the product.
Production costs are divided into:
- Direct Material
- Direct Labour
- Overheads
Companies generally want to cut down their expenses to increase their profit. As Revenue-Expenses= Profit.
Baadshah started a detective agency. This company provides a service, hence costs related to these companies are different compared to a manufacturing company. Similar to the scene that you saw, Ram Lal (played by Johnny lever) mentions:
Cost of Table= Rs. 10,000
2 Chairs= Rs. 2,000
2 Ashtrays= Rs. 900
Chandelier= Rs. 20,000
Misc Items= Rs. 1,000
Glass= Rs. 15,500
Clothes on Rent= Rs. 500
Total= Rs. 49,900
The above items mentioned are the costs incurred to generate revenue for the business. A company’s objective is to maximize its profit. Hence, profit can be increased when expenses are decreased. Expenses are recorded in the books in two ways: the Accrual concept method and the cash method.
How are expenses recorded?
Expenses are recorded in the books of accounts in the income statement. Under the cash accounting system, expenses are recorded as soon as the expenses are paid. While under the accrual accounting system, expenses are recorded, when they are incurred. Expenses are debited in the income statement. This comes from the rule of a journal entry that says: debit all expenses and credit all incomes.
For example, if a business orders transport services. Under the cash basis system, the company would record it when the bill is paid. While on an accrual basis, the accountant would record the entry only when the services are availed.
Types of Expenses:
Expenses can be of two types: Operating and Non-operating expenses. Operating expenses are those that are related to a business’s core activity. Example: COGS ( Cost of goods sold), Selling, general and administration costs (SG&A), telephone or Internet expenses, etc.
Non-operating expenses are those expenses that are not directly related to the core activity of the business. These expenses are not used in the calculation of EBIT. For example Interest expenses, lawsuit expenses, etc.
Format of Income Statement:
Let’s consider the Baadshah detective agency’s income statement. It would look like this in the books of accounts. Currently, they made a profit of Rs. 100. It could have been nil or negative (loss) if expenses went above Rs. 50,000.









[…] expenses are large in nature and are reported in the income statement of the company. Rent expenses are debited to the profit and loss account or the income […]
[…] loss occurs when expenses are higher than the revenue/sales of the company. This is reflected on the financial statement […]
[…] Telephone expenses […]
[…] debts are expenses for the banks or any other lender. Bad debts occur when an individual/business is not able to […]
[…] are those goods that are directly traceable to the goods or services being produced. The costs of these materials can be directly charged to products because physical observation can be used to […]