Movie Case Study
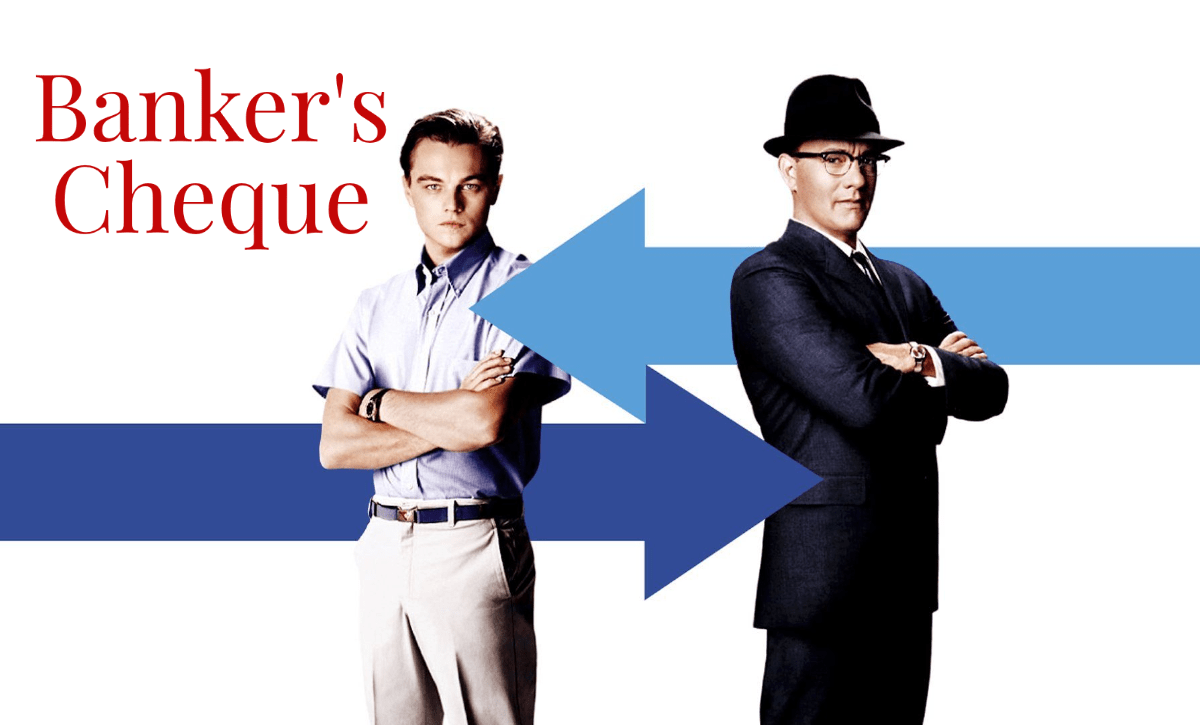
The scene you just saw shows how Frank Abagnale (played by Leonardo di Caprio) is taking out different amounts of Cashier’s cheques from his blazer and going outside to encash them. At this time Cheryl Ann (played by Jennifer Garner) interrupts him and asks him to endorse the cashier’s cheque to her.
In this blog, Learning Perspectives will explore the meaning of a Bankers cheque.
Bankers Cheques – What are they? How do you use them?
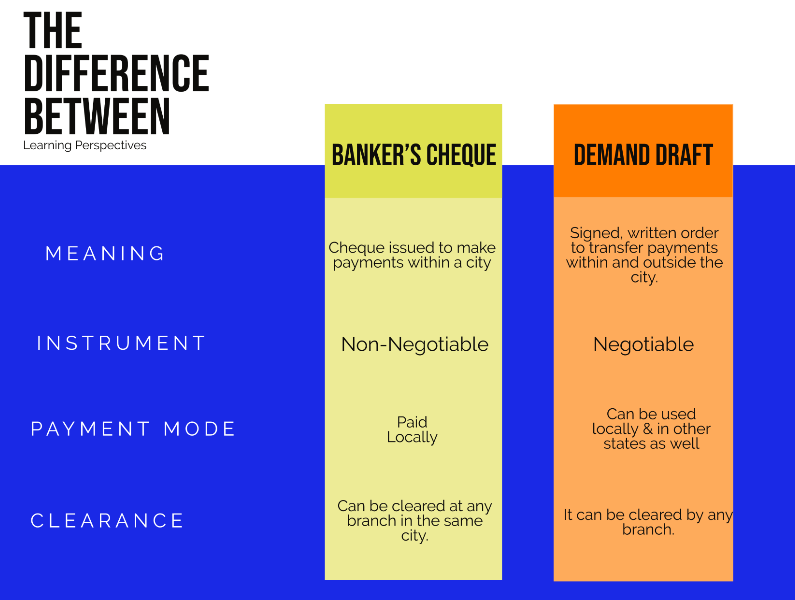
In India, a cashier’s cheque is called a Banker’s cheque or a pay order. As the name suggests banker’s cheque means a cheque issued by the bank itself. It is a non-negotiable instrument, an order to pay in the same city.
If you need to make a payment to a University or an institute, they can ask you to issue a banker’s cheque or a demand draft (DD/PO) instead of writing a personal cheque. This means that you will pay the bank the money and the bank will issue a pay order or a banker’s cheque on your behalf. This is an assured payment as the bank itself is issuing it. Universities and big institutes generally prefer these demand drafts and pay orders as they know this will not bounce or be dishonored.
If you write a personal cheque to the University, there is a chance that the cheque would bounce as there might be an insufficient balance in your account. These Universities and institutions don’t want to take that risk. Hence a demand draft and pay order/ banker’s cheque works best for them.
Parties in a Banker’s cheque
For a normal cheque, for which I may write to you, there are three parties,
- the one who issues the cheque is called the drawer,
- the one who receives the cheque is called the payee and,
- the bank on which it is drawn is called the drawee.
In the case of a Banker’s cheque, both the drawer and drawee are the same i.e. the bank itself unlike in the case of an ordinary cheque where the drawer is the customer.
A banker’s cheque is a cheque issued to make payments within a city. You may have heard of it being called a “cashier’s cheque” or “pay order“.
Uncertainty in Cheque Payments:
The uncertainty associated with cheque payment makes the mode unacceptable to some entities such as government departments and institutions. A bank issues a Pay order (PO) when it is sure to be paid because no bank can afford to default on losing money. Banks collect a fee for issuing PO.
Duration of Bankers’ Cheque:
Bankers’ cheque/ PO and demand draft (DD) both are valid for a 3-month period and one can’t use them after the end of 3 months. A PO is generally used for making local payments as it is payable at the place of its issue. DDs are used when payments have to be made to long-distance places and the payee insists on the certainty of the payment.
Endorsement:
If you watch the scene carefully, the actress asks Leonardo Di Caprio to endorse the cheque in her name. To endorse a cheque, he would have just had to write the name at the back of the cheque and sign it. While a banker’s cheque or a pay order cannot be endorsed to someone else. A banker’s cheque is a non-negotiable instrument and hence cannot be transferred or exchanged for cash. It can be cleared at any branch of the bank in the same city.
Difference between Bankers’ cheque and Demand Draft:
There are many types of cheques in the country and they all have their distinct features.
- Bearer Cheque
- Bankers Cheque
- Crossed Cheque
- Traveler’s Cheque
- Post-dated Cheques
- Mutilated Cheques
Understand Banker’s Cheque with a Video







[…] are other kinds of cheques too such as bankers’ cheque and multi-city […]
[…] Bill of exchange is a written document while a it is not a contract. It specifies the number of days in which the payment needs to be made. Bill of exchange can be accepted by the drawee to make the payment. If a bill of exchange is issued by a bank, then it is referred to as a bank draft. […]